Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) affects millions of individuals following exposure to traumatic events. Understanding available treatment resources can help individuals and their support systems make informed decisions about recovery approaches. Here is some information about established therapeutic interventions and emerging treatment options that research has shown to support PTSD recovery.
Understanding PTSD
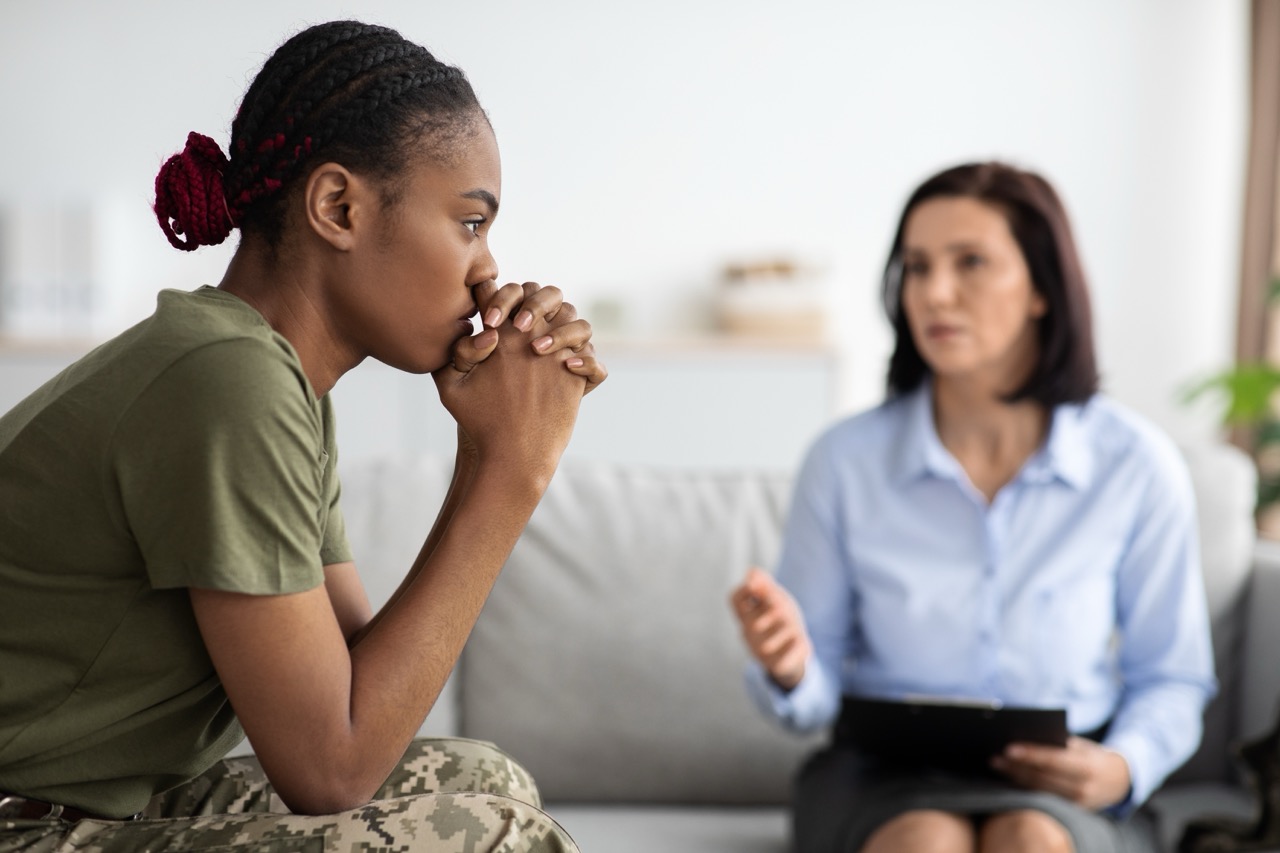
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that develops after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, such as natural disaster, an accident, combat, or personal assaults. It is marked by symptoms like intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, nightmares, heightened anxiety, and avoidance of trauma-related triggers. Emotional numbing, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and feelings of guilt or shame are also common. Recognizing PTSD is the first step toward seeking help, and early intervention can significantly improve quality of life.
Emerging Treatment Modalities
Recent research is exploring ketamine treatments for individuals with treatment-resistant PTSD. Unlike traditional antidepressants, ketamine targets the brain’s glutamate system and is administered under clinical supervision, often paired with psychotherapy. Researchers are working to refine dosing methods and combine therapies to enhance safety and effectiveness. This holistic approach aims to improve outcomes for those struggling with severe PTSD.
Traditional Therapeutic Approaches
Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) is a structured method that helps individuals identify and change trauma-related thoughts. Studies show that CPT significantly reduces symptoms in both veterans and civilians. By understanding unhelpful thought patterns, people can correct their thinking to process traumatic events more effectively.
Prolonged Exposure (PE) therapy involves gradual, controlled exposure to trauma-related memories and situations. This approach reduces avoidance behaviors and intrusive symptoms often linked to PTSD. Research highlights its success in helping patients confront and overcome trauma in a safe, supportive setting.
Medication can also be a valuable part of managing PTSD symptoms. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), like sertraline and paroxetine, help regulate brain chemicals affected by trauma. Prazosin is especially effective in reducing nightmares and improving sleep disturbances for PTSD patients.
Complementary Support Resources
Veteran organizations and community groups create valuable peer support networks, allowing individuals with shared trauma experiences to connect and share recovery strategies. Both in-person and online support groups provide safe spaces for participants to process their trauma alongside others who understand the challenges of PTSD recovery. These connections build a sense of belonging and understanding, which can significantly support the healing process.
Incorporating physical activity, mindfulness practices, and good sleep habits into PTSD treatment plans has been highly effective. These approaches complement traditional therapies by boosting overall well-being and reducing symptoms. Yoga and meditation, in particular, have proven to help trauma survivors by lowering hypervigilance and improving emotional balance. Together, these strategies offer a well-rounded approach to recovery.
Finding Professional Support for PTSD
Recovery from trauma is a personal journey that benefits from professional guidance and evidence-based treatment. Qualified mental health professionals tailor interventions to individual needs, considering factors like trauma type and co-occurring conditions. Specialized clinics and trauma-informed practitioners offer comprehensive care, providing access to a range of treatment options. With regular evaluation, treatment plans can be adapted to support progress and foster healing.